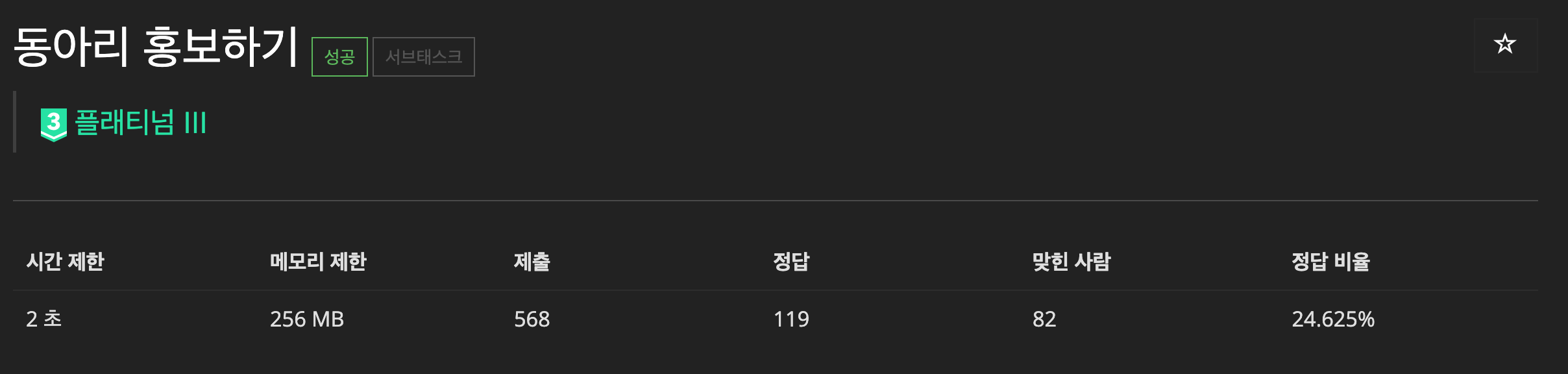
BOJ 17493 - 동아리 홍보하기
대개 이런 문제들은 Leaf 노드부터 위상정렬을 이용해 그리디하게 많이 푸는 편인데
이 문제는 Leaf의 부모가 항상 전단지가 붙어야된다 이후로 딱히 생각을 발전시키기 어려워 DP의 상태를 정의해 풀었다.
$dp[i][on_p][on_c]=i$ 에서 부모에 전단지가 붙은 상태 $op_p$ 이고 $i$에 전단지를 붙일건지 말건지가 $op_c$ 일 때 $i$의 서브트리에서 전단지를 붙이는 경우의 수이다.
$i$에 대해 상태는 $3$개만 있어도 되지만 $4$개로 정의했다.
다른 경우는 그냥 자식들에서 적절히 구해주면 되고 $on_p=0 ~ \& ~ on_c=0$ 인 상태를 보자.
자식이 하나도 없다면 불가능하므로 $\infty$를 반환한다.
$\text{Optimal}=\displaystyle \sum_{c \in Child(i)} ~ \text{Min}(dp[c][0][0],dp[c][0][1])$ 이라 할 때,
Optimal을 그대로 써주려면 최소 하나의 자식이 $dp[c][0][1] \le dpc[c][0][0]$ 이여야 한다.
이 경우엔 Optimal을 그대로 반환해주고,
그렇지 않다면 $Min_{c \in Child(i)} dp[c][0][1] - dp[c][0][0]$ 을 Optimal에 더해서 반환한다.
그리디하게 가장 비용이 적게 증가하는 자식 하나에 전단지를 붙이는 경우로 선택해준다는 의미이다.
const int inf = 3e5;
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vvi edges(n);
for (int i = 0, u, v; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v, u--, v--;
edges[u].pb(v), edges[v].pb(u);
}
vi vis(n);
vector<vvi> dp(n, vvi(2, vi(2, -1)));
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
function<void(int, int, int, int)> fn = [&](int cur, int p_on, int c_on, int p) -> void {
vis[cur] = 1;
int &ret = dp[cur][p_on][c_on];
if (~ret) return;
ret = 0;
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
fn(to, 0, 0, cur);
fn(to, 0, 1, cur);
fn(to, 1, 0, cur);
fn(to, 1, 1, cur);
}
if (p_on) {
// 부모도 켜져있고 나도 키는경우
if (c_on) {
ret++;
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
ret += min(dp[to][1][0], dp[to][1][1]);
}
assert(ret < inf);
} else {
// 부모는 켜져있는데 내가 안키는 경우
// 나는 상관없지만, 자식은 안키려면 다른것한테 받아야한다.
//
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
ret += min(dp[to][0][0], dp[to][0][1]);
}
assert(ret < inf);
}
} else {
// 부모가 꺼져있는데 내가 키는경우
if (c_on) {
ret++;
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
ret += min(dp[to][1][0], dp[to][1][1]);
}
assert(ret < inf);
} else {
// 부모가 꺼져있고 나도 꺼져있는 경우
// 최소한 하나의 자식이 1이여야 한다.
// 그럴 수 없다면 inf 반환
int optimal = 0, is_leaf = 0;
int can_use_one = 0;
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
is_leaf = 0;
optimal += min(dp[to][0][0], dp[to][0][1]);
if (dp[to][0][1] <= dp[to][0][0]) can_use_one = 1;
}
assert(optimal < inf);
if (is_leaf) ret = inf;
else {
if (can_use_one) ret = optimal;
else {
int mn_diff = inf;
for (int to: edges[cur]) {
if (to == p) continue;
mina(mn_diff, dp[to][0][1] - dp[to][0][0]);
}
ret = optimal + mn_diff;
}
}
}
}
};
fn(i, 0, 0, -1);
fn(i, 0, 1, -1);
ans += min(dp[i][0][0], dp[i][0][1]);
}
cout << ans;
}



Comments